
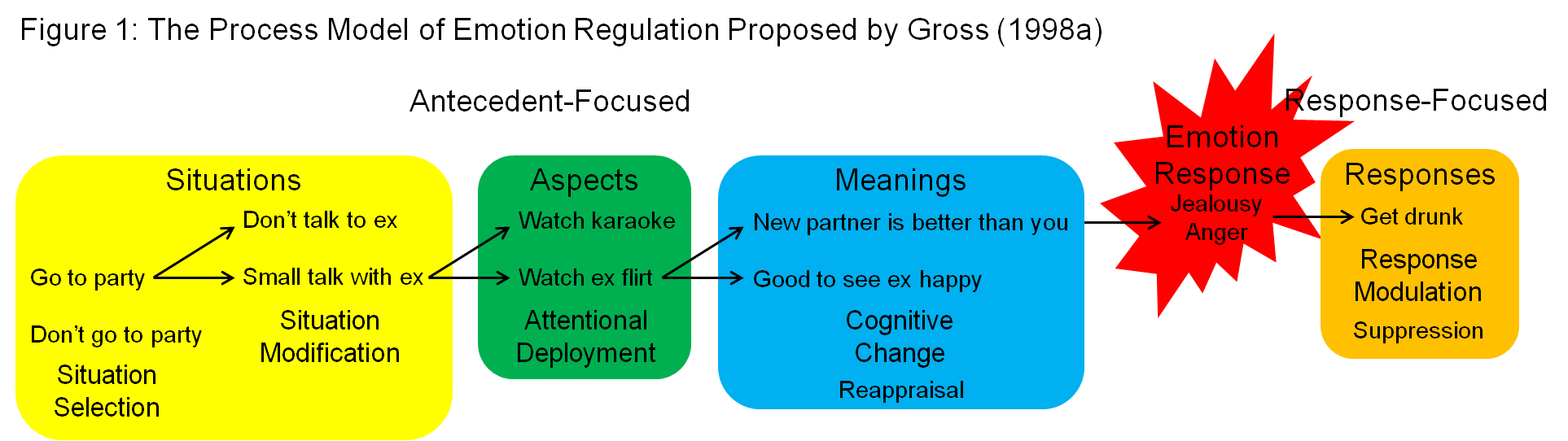
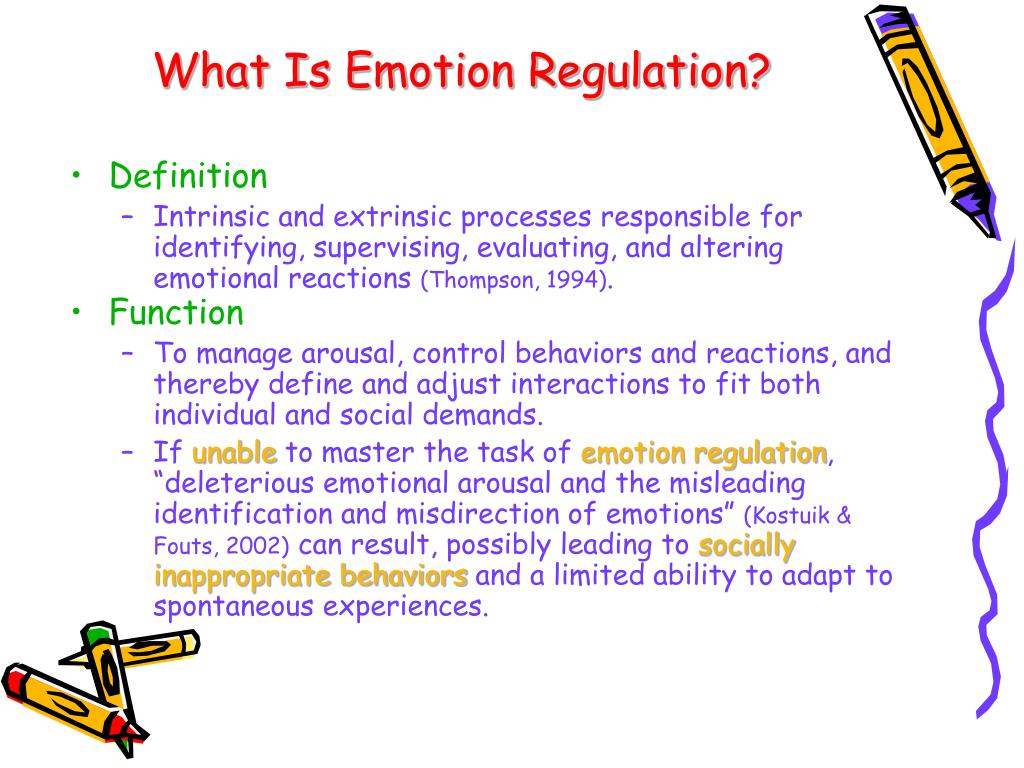
IntroductionĮmotion regulation is a growing area of interest for theorists and researchers alike, with adolescent studies steadily increasing over the past decade. Preliminary results suggest that yoga increases emotion regulation capacities of middle adolescents and provides benefits beyond that of PE alone. No significant relationship was discovered between the changes in emotion regulation and the proposed mediating variables.
Pre-post data analyses revealed that emotion regulation increased significantly in the yoga group as compared to the PE group ( (1,32) = 7.50,, and eta 2 =. High school students were randomized to participate in a 16-week yoga intervention ( ) or regular PE ( ). In addition, the potential mediating effects of mindful attention, self-compassion, and body awareness on the relationship between yoga and emotion regulation were examined. This study was designed to evaluate the impact of a yoga intervention on the emotion regulation of high school students as compared to physical education (PE). A discipline such as yoga offered during school may increase emotion regulation, but research in this area is lacking. Emotion dysregulation contributes to a variety of psychosocial difficulties in this population. Middle adolescents (15–17 years old) are prone to increased risk taking and emotional instability.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
